Franklin's Kite Experiment
Benjamin Franklin flew a kite in a thunderstorm to prove that lightning is electrical in nature, a pivotal moment in the study of electricity.
Explore key moments in the evolution of electronics, from the earliest discoveries to modern innovations.

Benjamin Franklin flew a kite in a thunderstorm to prove that lightning is electrical in nature, a pivotal moment in the study of electricity.

Alessandro Volta invents the voltaic pile, the first true battery, providing a continuous source of electricity for experimentation and application.

Michael Faraday's discovery laid the groundwork for electric motors, transformers, and all of modern electrical engineering.

Willoughby Smith discovered selenium's photoconductivity, later important in photocells and solar panels.

Alexander Graham Bell invents the telephone, enabling real-time voice communication over long distances for the first time.

Thomas Edison improves and patents the practical incandescent light bulb, revolutionizing lighting across the world.

Heinrich Hertz proves the existence of radio waves, laying the foundation for wireless communication technologies.

John Ambrose Fleming invents the first vacuum tube diode, enabling signal detection in radios.
Reginald Fessenden makes the first radio audio broadcast, ushering in the era of wireless mass communication.

The first successful demonstration of a fully electronic television system marks a new chapter in visual media and entertainment.
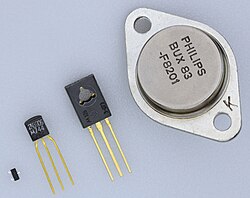
Bardeen, Brattain, and Shockley create the first transistor at Bell Labs — marking the birth of modern electronics.
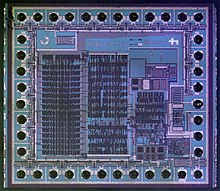
Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce independently invent the IC — enabling miniaturization and complexity in electronics.

Intel releases the 4004, the first microprocessor — a complete CPU on a single chip, powering early computers.

Introduction of the first widely available personal computers empowers individuals and small businesses with computing capabilities.

The first mobile phone goes on sale, changing communication forever and paving the way for mobile computing.

Tim Berners-Lee invents the World Wide Web, transforming the internet into a global platform for information and communication.
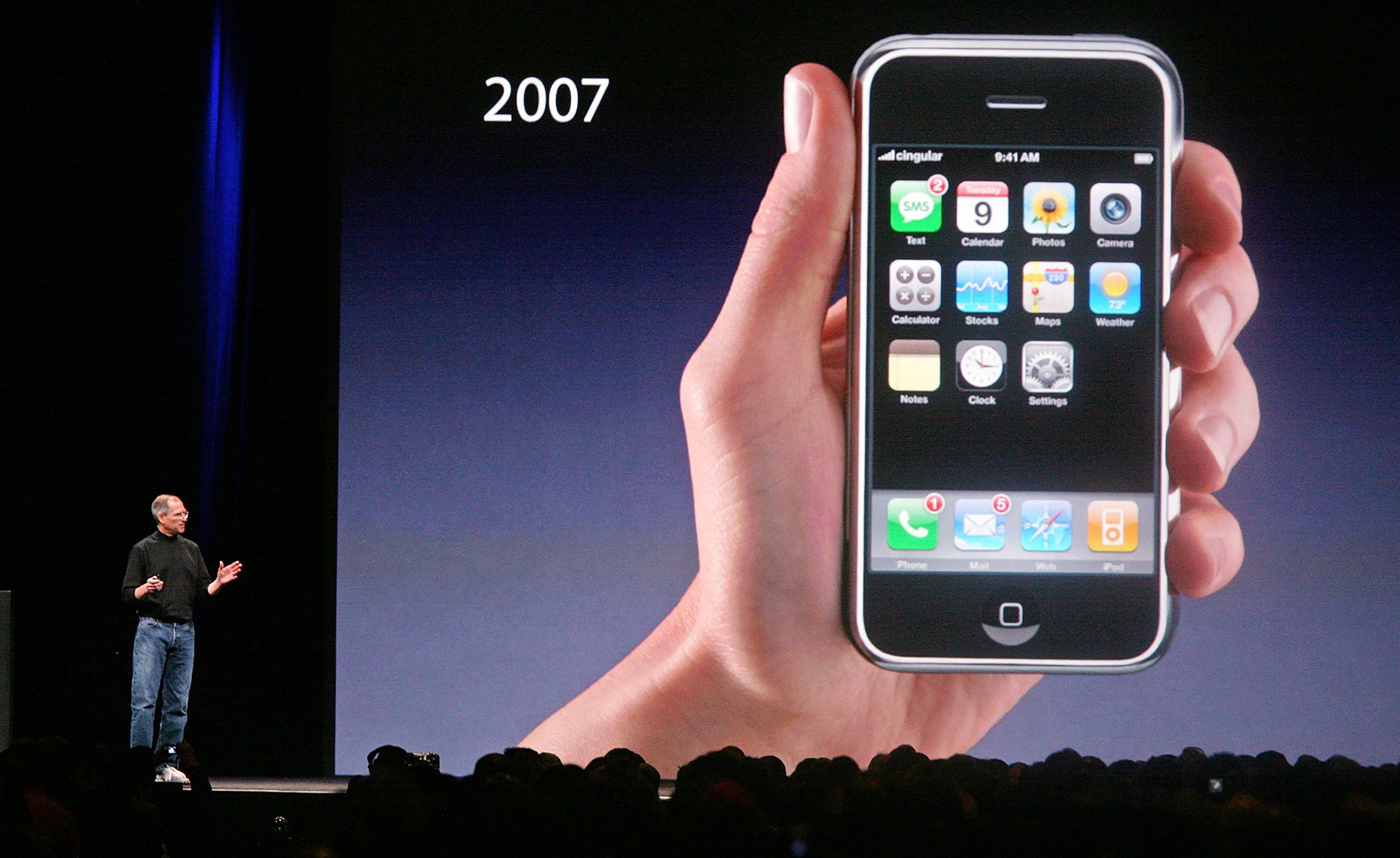

Apple introduces the iPhone, fusing communication, computing, and sensors — a leap forward in consumer electronics.

The rise of touchscreen tablets like the iPad creates a new category of mobile device, combining the portability of smartphones with larger screens.

Smartwatches and fitness trackers gain popularity, integrating computing into everyday accessories and enhancing personal health tracking.
The 2020s witness rapid advancement in artificial intelligence and early development of quantum computing, signaling a new era in electronics and computation.